Transmission Modes in Computer Networks

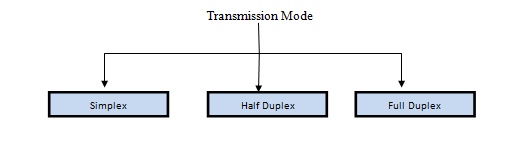
Transmission mode means transferring of data between two devices. It is also called communication mode. These modes direct the direction of flow of information. There are three types of transmission mode. They are :
- Simplex Mode
- Half duplex Mode
- Full duplex Mode
SIMPLEX Mode
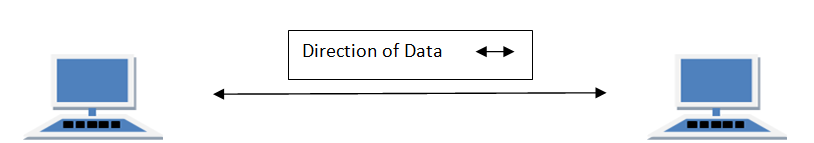
In this type of transmission mode data can be sent only through one direction i.e. communication is unidirectional. We cannot send a message back to the sender. Unidirectional communication is done in Simplex Systems.
Examples of simplex Mode is loudspeaker, television broadcasting, television and remote, keyboard and monitor etc.
HALF DUPLEX Mode
In half duplex system we can send data in both directions but it is done one at a time that is when the sender is sending the data then at that time we can’t send the sender our message. The data is sent in one direction.
Example of half duplex is a walkie- talkie in which message is sent one at a time and messages are sent in both the directions.
FULL DUPLEX Mode
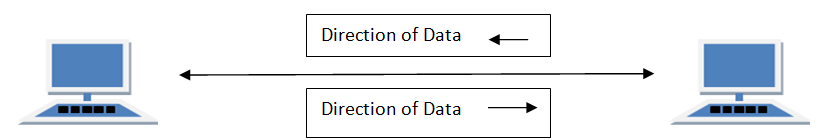
In full duplex system we can send data in both directions as it is bidirectional. Data can be sent in both directions simultaneously. We can send as well as we receive the data.
Example of Full Duplex is a Telephone Network in which there is communication between two persons by a telephone line, through which both can talk and listen at the same time.
In full duplex system there can be two lines one for sending the data and the other for receiving data.